What is Power Cable? Benefits and drawbacks
The cables used for the transmission and distribution of electrical energy cables are called electrical power cables.
It is used for the transmission of extra high voltages in a place. The power cable consists of two or more electrical conductors combined with an over sheath.
Underground cables are more costly than aerial cables. Electricity cables are primarily used for power distribution and transmission.
It is an assembly of one or more electrical conductors that have been individually insulated and are often held together by an overall sheath.
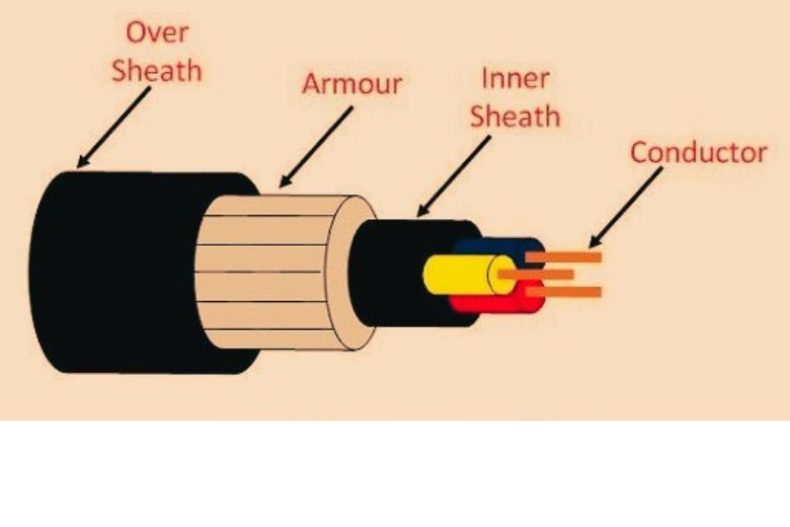
The power cables consist of three main components:
- Conductor
- Dielectric
- Armour
- Sheath
The conductor is used to provide the conducting path for the current.
The dielectric provides the service voltage and isolates the conductor from other objects.
The primary aim of armoring is to protect the current-carrying conductors from electromagnetic interference.
It is also used to earth the cable for security. The sheath is used to avoid contact with moisture entering and protects the cables from all external influences like fire chemical or electrochemical attack. etc.
The key benefits are as below:
- The project is hidden, and the power wire is buried underground, so it little affects how the city looks. Even in the event of an accident, personal safety is typically unaffected.
- The high cable capacitance might increase the line power factor.
- The reliability of its power supply is strong despite the influence of outside variables (such as lightning, wind damage, bird damage, etc.)
The drawbacks are as below:
- Finding the fault is challenging and dealing with the disaster quickly is a hassle.
- Cable joints require a complex fabrication technique.
- high cost, significant upfront investment in construction, and a ten-fold increase in investment in cable lines compared to overhead lines with the same voltage level;