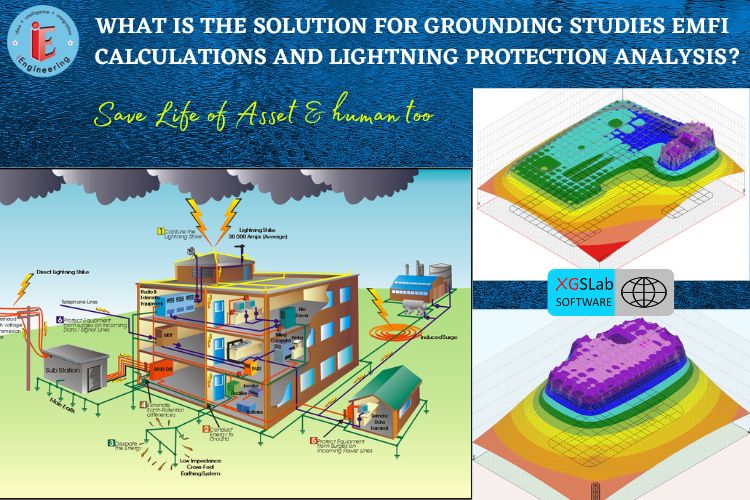
INTRODUCTION:
XGSLab software was first developed in 1990, and the first module became accessible in 2005. Since then, XGSLab has seen constant improvement in all areas, including performance, usability, and 2D/3D graphics output. FOR POWER, GROUNDING, AND LIGHTNING PROTECTION SYSTEMS: ELECTROMAGNETIC SIMULATION One of the most potent electromagnetic simulation programmes available is called XGSLab (or simply XGS). It is the only product on the market that considers American (IEEE Std 80-2013), European (EN 50522:2010), and International (IEC/TS 60479-1:2018) Standards when analysing grounding systems.
XGS INCLUDES THE MODULES:
GSA (Grounding System Analysis) is a basic application for underground systems
GSA_FD (Grounding System Analysis in the Frequency Domain) have general applications with underground systems
XGSA_FD (Over and Underground System Analysis in the Frequency Domain) have general applications for overhead and underground systems
XGSA_TD (Over and Underground System Analysis in the Time Domain) have general applications for overhead and underground systems.
NETS (Network Solver) is solver for multi-conductor and multi-phase full meshed networks.
SHIELD is a powerful full 3D graphical application for the evaluation of the protection of structures from direct lightning strokes by using the Rolling Sphere and by the Eriksson method.
GENERAL INFORMATION ABOUT XGSLAB:
XGSLab has got a broad field of application because the implemented calculation model is for general use and solves the Maxwell’s equations considering the earth effects by Sommerfeld integrals.
- Now, step voltage calculations may be performed using 0.25 m (0.82021 ft) long steps.
- Implemented a new seasonal analysis that enables taking into account how a location’s projected temperature may affect how the soil model is applied.
- We ran a speed test, and the result showed the quickest response. We discovered that the built-in computer programme is the fastest. To achieve this High Speed in Calculation in XGSLab, follow these instructions:
1. Algorithms optimization
2. Parallel Computing
- As the industry standard for high-speed 3D vector graphics used in CAD, virtual reality, scientific visualisation, and flight simulation, we have begun to create a new graphic based on OpenGL.
- Each module comes with a soil analysis tool that, using measured soil resistivity data and an additional soil covering layer, can construct a uniform or double layer soil model.
- The programme can import a “dxf” file with one or more electrodes in any number and shape. In order to automatically recognise the connection between conductors and create the incidence matrix, GSA FD and XGSA FD also need to be aware of the topology of the electrodes.
- All modules offer the option to select a language and include libraries with common material features (English, German, Spanish, Italian and French).
XGS ESSENTIALLY CAN BE USED TO THE CALCULATION OF:
- GROUNDING SYSTEMS
- CATHODIC PROTECTION SYSTEMS
- ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS
- ELECTROMAGNETIC INTERFERENCES
- FAULT CURRENTS DISTRIBUTION
- LIGHTNING PROTECTION SYSTEMS
XGSLAB REQUIRES THE FOLLOWING SET OF INPUT DATA:
- REFERENCE STANDARD (IEC, EN, iEEE-80)
- SOIL DATA (soil model and parameters)
- LAYOUT DATA (geometry, topology and cross sections)
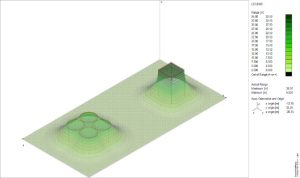
- ELECTRICAL DATA (injected currents or imposed EMF) Output results depend on the module in use and in any case are available in numerical or graphical format. XGSLab produces professional colour graphics based on orthographic or isometric projections ready to be used in engineering reports.
MORE DETAILS ABOUT MODULES
GSA
GSA is a widely used and respected module for designing and calculating earth grids, including analyses of soil resistivity. The grounding system analysis, or GSA, is based on a PEEC static numerical model and the equipotential condition of the electrodes. It can analyse the low frequency performance of a grounding system made up of numerous distinct electrodes of any shape but with a small number of them into a uniform or multilayer soil model.
Output results:

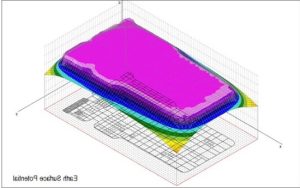
GSA_FD
The most advanced grounding programme is GSA FD, a module for earth grid calculation and design in the frequency domain that includes soil resistivity analysis. GSA FD, which is based on the PEEC full wave numerical model, can be used in a variety of situations with systems made up of numerous distinct electrodes of any shape, size, and type of conductor (solid, hollow, stranded, and coated or bare) placed into a uniform, multilayer or multizone soil model over a wide frequency range, from DC to approximately 100 MHz. Additionally, it is crucial to keep in mind that GSA FD can take into account the frequency dependency of soil characteristics according to several models and in the model with a consensus indication in the CIGRE TB 781 2019
Output results:
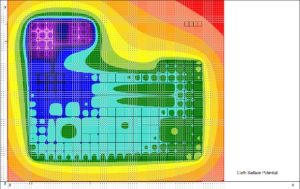
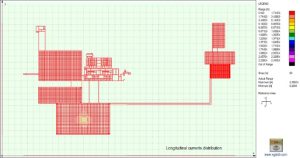
XGSA_FD
The GSA FD application field is expanded to include overhead systems by XGSA FD. Additionally, XGSA FD can be used in general settings in the same frequency range as GSA FD and is based on a PEEC full wave numerical model. Catenary conductors and bundle conductors can also be managed by XGSA FD, and sources where potential or leakage current and longitudinal current are pushed and independent by other factors can also be taken into consideration. For these reasons, XGSA FD is likely one of the most potent and versatile tools available for this type of calculation.
Output results:
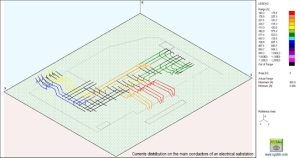
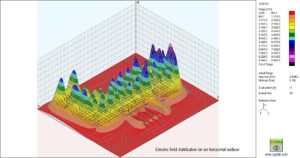
XGSA_TD
A strong module called XGSA TD expands the application field of XGSA FD to the time domain. XGSA FD employs the so-called “frequency domain technique” in this regard. This method is exacting and enables for the frequency dependency of soil properties to be taken into account. As is well known, a transient can be thought of as the superposition of several waveforms with a single frequency that have been calculated using forward fast fourier transforms (FFT).
Output results:
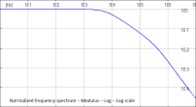
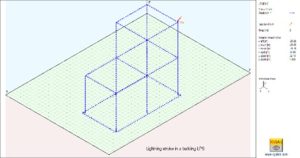
NETS
NETS is a very adaptable tool that can solve fully mesh multi-phase and neutral conductor networks while taking into account both the earth path and all other neutral conductor paths. Kirchhoff rules for multi-conductor, multi-phase systems are the foundation of NETS. It can be used to represent power systems as multi-conductor networks, overcoming the limitations of the traditional symmetrical components method and allowing for the consideration of asymmetrical and/or unbalanced systems even in the presence of grounding circuits or circuits with a different number of phases.
Output results:
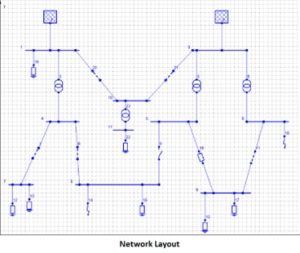
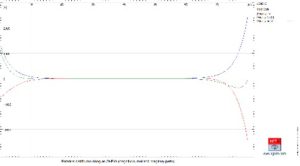
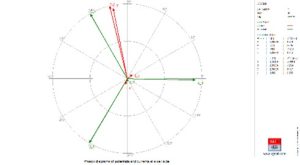 SHIELD
SHIELD
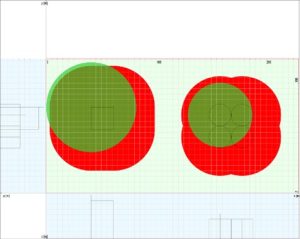
SHIELD takes into account American (IEEE Std 998-2012), European (EN 62305-3:2012), and international (IEC 62305-3:2012) standards. When the Rolling Sphere Method is activated, SHIELD first creates a 3D surface that corresponds to every place that might be touched as the sphere rolls over the air termination system.
Output results:
For more details or inquiries kindly reach us at
jyotig@iengaust.com.au or enquiries@iengaust.com.au
For deep details we can arrange Free Demo for Software XGSLab
Visit our software page https://ieng.tech/xgslab-earthing-emfi-lightning-analysis/